Estimated read time: 3-4 minutes
This archived news story is available only for your personal, non-commercial use. Information in the story may be outdated or superseded by additional information. Reading or replaying the story in its archived form does not constitute a republication of the story.
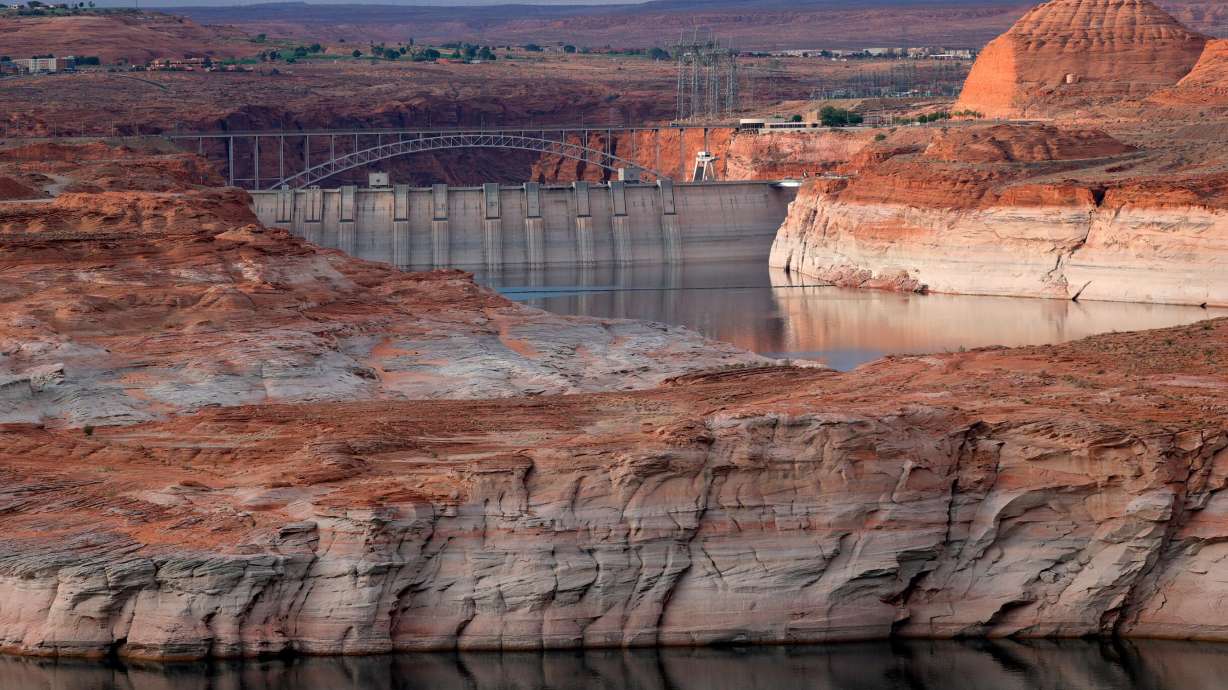
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The falling water levels at Lake Powell, the second-largest man-made reservoir in the U.S., could make the dam's hydroelectric power generation impossible as soon as next year, according to new projections released Wednesday by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation.
The new modeling shows a 3% chance that Lake Powell, which is located on the Colorado River from northern Arizona to southern Utah, could drop below the minimum level needed to allow the lake's Glen Canyon Dam to generate hydroelectricity next year.
In 2023, the chance of a shutdown grows to 34%, according to the projection.
When running at full capacity, the dam produces power that is distributed to some 5.8 million homes and businesses spanning from Nebraska to Nevada.
"The latest outlook for Lake Powell is troubling," said Reclamation's Upper Colorado Basin Regional Director Wayne Pullan in a news release. "This highlights the importance of continuing to work collaboratively with the Basin States, Tribes and other partners toward solutions."
Lake Powell and nearby Lake Mead, the nation's largest reservoir, have drained at an alarming rate this year. The two reservoirs fed by the Colorado River watershed provide a critical supply of drinking water and irrigation for many across the region, including rural farms, ranches and native communities.
In late July, Lake Powell had fallen to roughly 3,554 feet in elevation — just 33% of capacity — according to the US Bureau of Reclamation, below the previous all-time low set in 2005.
The latest outlook for Lake Powell is troubling.
–Wayne Pullan, Upper Colorado Basin regional director
The projections for water levels in Lake Mead, which provides water to 25 million people in the West, are also bleak as climate change, drought and poor runoff continue to sap the river's supply.
In 2025, the updated projections now show a 66% chance that Lake Mead could drop below the critical threshold of 1,025 feet above sea level. If water levels stay below that threshold, it would trigger deep water cuts, potentially affecting millions of people in California, Arizona, Nevada and Mexico.
There is also a greater than 1-in-5 chance that water levels in Lake Mead will fall below 1,000 feet above sea level in 2025. That is barely 100 feet above what is considered "dead pool," the level at which water can no longer flow through Hoover Dam.
Related:
The new models come just over a month after the Colorado River system's first-ever shortage was declared, triggering water cuts that will be felt next year in Arizona, Nevada and Mexico.
Drought is evaporating water resources
The Colorado River Basin and much of the Southwest are in the midst of a climate change-fueled megadrought, which has stretched on for more than 20 years.
A study published in the journal Science in 2020 found that the period from 2000-2018 was the driest 19-year stretch since the late 1500s.
And matters have only gotten worse in the years since. The dryness the region has experienced from 2020 and into 2021 is designated as exceptional — the most severe level of drought — in both the paleoclimate and historical records, according to a study published Tuesday by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's drought task force.
California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico experienced exceptional drought since 2020, the study shows. It found that the current drought is expected to continue into 2022 and perhaps beyond.
As drought conditions cause water levels to drop, billions of kilowatt hours of hydroelectricity that power homes from Nebraska to Arizona are also at risk.