Estimated read time: 3-4 minutes
This archived news story is available only for your personal, non-commercial use. Information in the story may be outdated or superseded by additional information. Reading or replaying the story in its archived form does not constitute a republication of the story.
WASHINGTON — U.S. officials have approved the first over-the-counter birth control pill, which will let American women and girls buy contraceptive medication from the same aisle as aspirin and eyedrops.
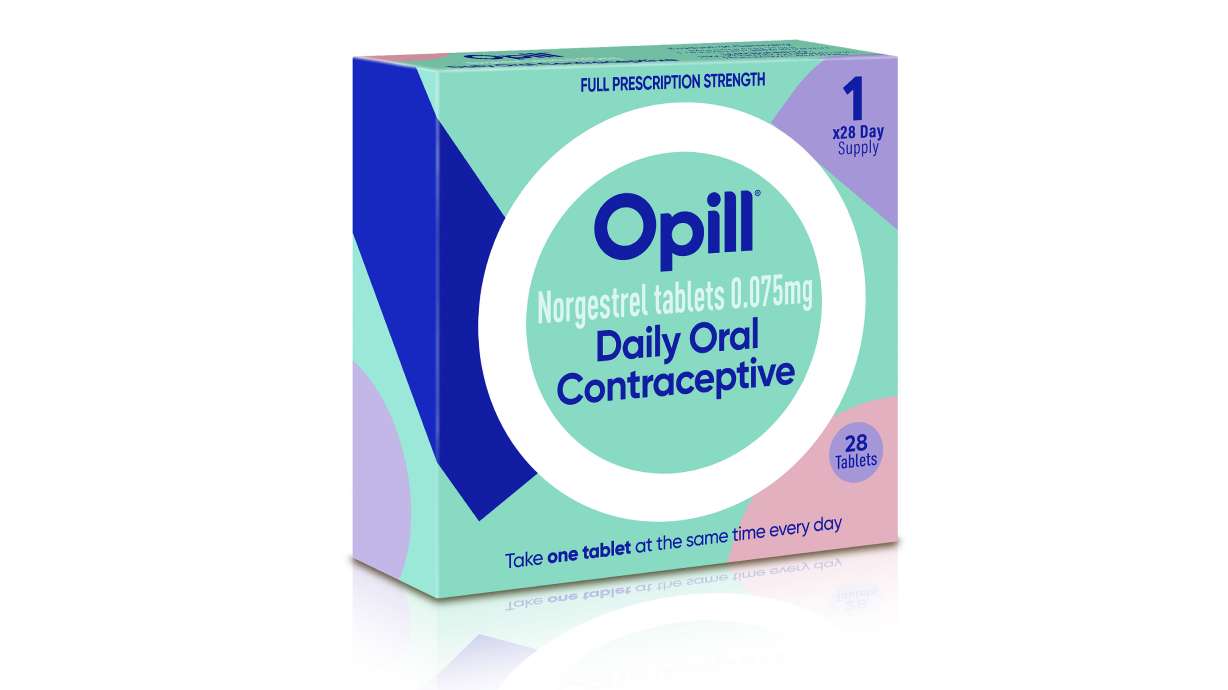
The Food and Drug Administration said Thursday it cleared Perrigo's once-a-day Opill to be sold without a prescription, making it the first such medication to be moved out from behind the pharmacy counter. The company won't start shipping the pill until early next year, and there will be no age restrictions on sales.
Hormone-based pills have long been the most common form of birth control in the U.S., used by tens of millions of women since the 1960s. Until now, all of them required a prescription.
Medical societies and women's health groups have pushed for wider access, noting that an estimated 45% of the 6 million annual pregnancies in the U.S. are unintended. Teens and girls, women of color and those with low incomes report greater hurdles in getting prescriptions and picking them up.
Some of the challenges can include paying for a doctor's visit, getting time off from work and finding child care.
"This is really a transformation in access to contraceptive care," said Kelly Blanchard, president of Ibis Reproductive Health, a nonprofit group that supported the approval. "Hopefully this will help people overcome those barriers that exist now."
Ireland-based Perrigo did not announce a price. Over-the-counter medicines are generally much cheaper than prescriptions, but they aren't covered by insurance.
Many common medications have made the switch to nonprescription status in recent decades, including drugs for pain, heartburn and allergies.
Perrigo submitted years of research to the FDA to show that women could understand and follow instructions for using the pill. Thursday's approval came despite some concerns by FDA scientists about the company's results, including whether women with certain underlying medical conditions would understand they shouldn't take the drug.
The FDA's action only applies to Opill. It's in an older class of contraceptives, sometimes called minipills, that contain a single synthetic hormone and generally carry fewer side effects than more popular combination hormone pills.
But women's health advocates hope the decision will pave the way for more over-the-counter birth control options and, eventually, for abortion pills to do the same.
That said, the FDA's decision has no relation to the ongoing court battles over the abortion pill mifepristone. The studies in Perrigo's FDA application began years before the Supreme Court's reversal of Roe v. Wade, which has upended abortion access across the U.S.
With some states curtailing women's reproductive rights, the FDA has faced pressure from Democratic politicians, health advocates and medical professionals to ease access to birth control. The American Medical Association and the leading professional society for obstetricians and gynecologists backed Opill's application for over-the-counter status.
An outside panel of FDA advisers unanimously voted in favor of the switch at a hearing in May where dozens of public speakers called for Opill's approval.
Advocates were particularly interested in Opill because it raised fewer safety concerns. The pill was first approved in the U.S. five decades ago but hasn't been marketed here since 2005.
"It's been around a long time, and we have a large amount of data supporting that this pill is safe and effective for over-the-counter use," said Blanchard, of Ibsis Reproductive Health.
Newer birth control pills typically combine two hormones, estrogen and progestin, which can help make periods lighter and more regular. But their use carries a heightened risk of blood clots, and they shouldn't be used by women at risk for heart problems, such as those who smoke and are over 35.
Opill has only progestin, which prevents pregnancy by blocking sperm from reaching the cervix. It must be taken around the same time daily to be most effective.
Perrigo executives said the company will spend the rest of the year manufacturing the pill and its packaging so it can be available in stores nationwide and online by early next year.