- The Rev. Jesse Jackson, civil rights leader and Martin Luther King Jr.'s protege, died at 84.
- Jackson, known for his advocacy, led the Rainbow/PUSH Coalition for social change.
- He ran for president twice, influencing future minority candidates like Barack Obama.
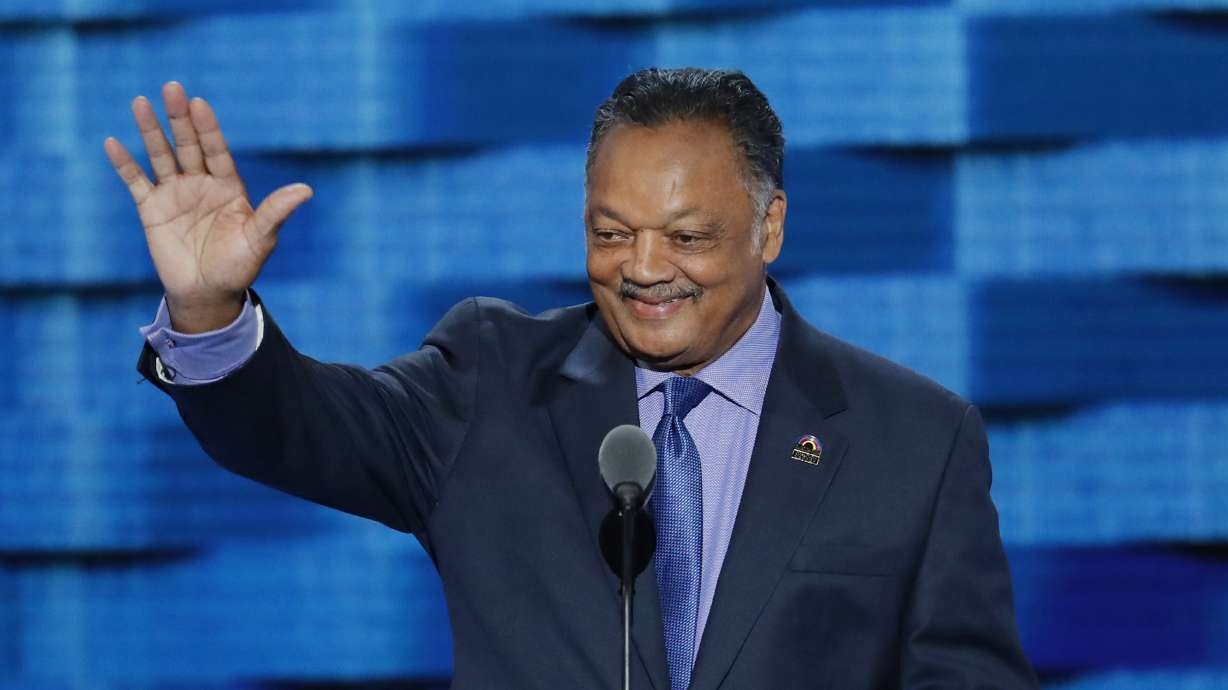
CHICAGO — The Rev. Jesse L. Jackson, a protege of the Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. and two-time presidential candidate who led the Civil Rights Movement for decades after the revered leader's assassination, died Tuesday. He was 84.
As a young organizer in Chicago, Jackson was called to meet with King shortly before King was killed, and he publicly positioned himself thereafter as King's successor.
Jackson led a lifetime of crusades in the United States and abroad, advocating for the poor and underrepresented on issues from voting rights and job opportunities to education and health care. He scored diplomatic victories with world leaders, and through his Rainbow/PUSH Coalition, he channeled cries for Black pride and self-determination into corporate boardrooms, pressuring executives to make America a more open and equitable society.
And when he declared, "I am Somebody," in a poem he often repeated, he sought to reach people of all colors. "I may be poor, but I am Somebody; I may be young; but I am Somebody; I may be on welfare, but I am Somebody," Jackson intoned.
It was a message he took literally and personally, having risen from obscurity in the segregated South to become America's best-known civil rights activist since King.
Santita Jackson confirmed that her father died at home in Chicago, surrounded by family.
"Our father was a servant leader — not only to our family, but to the oppressed, the voiceless, and the overlooked around the world," the Jackson family said in a statement posted online. "We shared him with the world, and in return, the world became part of our extended family."
Fellow civil rights activist the Rev. Al Sharpton said his mentor "was not simply a civil rights leader; he was a movement unto himself."
Calls to action, delivered in a memorable voice
Jackson's voice, infused with the stirring cadences and powerful insistence of the Black church, demanded attention. On the campaign trail and elsewhere, he used rhyming and slogans such as: "Hope not dope" and "If my mind can conceive it and my heart can believe it, then I can achieve it," to deliver his messages.
Jackson had his share of critics, both within and outside of the Black community. Some considered him a grandstander, too eager to seek out the spotlight. Looking back on his life and legacy, Jackson told the Associated Press in 2011 that he felt blessed to be able to continue the service of other leaders before him and to lay a foundation for those to come.
"A part of our life's work was to tear down walls and build bridges, and in a half century of work, we've basically torn down walls," Jackson said. "Sometimes when you tear down walls, you're scarred by falling debris, but your mission is to open up holes so others behind you can run through."
In his final months, as he received 24-hour care, he lost his ability to speak, communicating with family and visitors by holding their hands and squeezing.
"I get very emotional knowing that these speeches belong to the ages now," his son, Jesse Jackson Jr., told the AP in October.
A student athlete drawn to the Civil Rights Movement
Jesse Louis Jackson was born on Oct. 8, 1941, in Greenville, South Carolina, the son of high school student Helen Burns and Noah Louis Robinson, a married man who lived next door. Jackson was later adopted by Charles Henry Jackson, who married his mother.
Jackson was a star quarterback on the football team at Sterling High School in Greenville and accepted a football scholarship from the University of Illinois. But after he reportedly was told Black people couldn't play quarterback, he transferred to North Carolina A&T in Greensboro, where he became the first-string quarterback, an honor student in sociology and economics, and student body president.
Arriving on the historically Black campus in 1960 just months after students there launched sit-ins at a whites-only diner, Jackson immersed himself in the blossoming Civil Rights Movement.
By 1965, he joined the voting rights march King led from Selma to Montgomery, Alabama. King dispatched him to Chicago to launch Operation Breadbasket, a Southern Christian Leadership Conference effort to pressure companies to hire Black workers.
Jackson called his time with King "a phenomenal four years of work."
Jackson was with King on April 4, 1968, when the civil rights leader was slain at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee. Jackson's account of the assassination was that King died in his arms.
With his flair for the dramatic, Jackson wore a turtleneck he said was soaked with King's blood for two days, including at a King memorial service held by the Chicago City Council, where he said: "I come here with a heavy heart because on my chest is the stain of blood from Dr. King's head."
However, several King aides, including speechwriter Alfred Duckett, questioned whether Jackson could have gotten King's blood on his clothing. There are no images of Jackson in pictures taken shortly after the assassination.
Presidential aspirations fall short but help 'keep hope alive'
Despite once telling a Black audience he would not run for president "because white people are incapable of appreciating me," Jackson ran twice and did better than any Black politician had before President Barack Obama, winning 13 primaries and caucuses for the Democratic nomination in 1988, four years after his first failed attempt.
His successes left supporters chanting another Jackson slogan, "Keep Hope Alive."
"I was able to run for the presidency twice and redefine what was possible; it raised the lid for women and other people of color," he told the AP. "Part of my job was to sow seeds of the possibilities."
U.S. Rep. John Lewis said during a 1988 C-SPAN interview that Jackson's two runs for the Democratic nomination "opened some doors that some minority person will be able to walk through and become president."
Jackson also pushed for cultural change, joining calls by NAACP members and other movement leaders in the late 1980s to identify Black people in the United States as African Americans.
"To be called African Americans has cultural integrity — it puts us in our proper historical context," Jackson said at the time. "Every ethnic group in this country has a reference to some base, some historical cultural base. African Americans have hit that level of cultural maturity."